Multi Threading:-Ø
A
single program performing multiple actions in a symaltencily is known as Multi
Threading. Traditionally we come accrues a concept multi tasking. In which more
then one program can execute at a given point of time.
 System
Threading.Thread(<Method Name>)
System
Threading.Thread(<Method Name>)
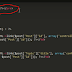
 Add a class ThreadDemo.cs
Add a class ThreadDemo.cs
 Add a class ThreadDemo.cs and
write the following code.
Add a class ThreadDemo.cs and
write the following code.
 using System;
using System;
 using System;
using System;
C,C++,Python, MFC, Multi Threading, ORACLE, BIG DATA,HADOOP
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
Vi Editor
VI EDITOR Move move in the editor: h right j up k down l left move top shift +g gg down the line of the file :8 go to line 8 search /string...
-
VI EDITOR Move move in the editor: h right j up k down l left move top shift +g gg down the line of the file :8 go to line 8 search /string...
-
1. Download XAMP and install as per your system configuration Link https://www.apachefriends.org/download.html 2. Editor for cake...

No comments:
Post a Comment